Bleeding Gums: Causes, Treatments, and Prevention
- June 09, 2025
- by
- Shanaya
Last Updated on June 21, 2025 by Shanaya
Bleeding gums can worry anyone. This often means there is gum inflammation, also known as gingivitis. If left unchecked, it can progress into serious gum disease like periodontitis. Early care at home and professional treatment both play key roles in stopping gums from bleeding. Along the way, good oral hygiene and proper nutrition protect your happy smile.
In this article, you will learn what causes bleeding gums, how to treat them at home, when to see a dentist, and how to prevent future problems.
What Are Bleeding Gums?
Bleeding gums mean your gums bleed easily, usually while brushing, flossing or eating. It usually happens when the gums are weak, swollen, or not healthy. This may indicate gum irritation, inflammation, or early sign of gum problems.
What Causes Bleeding Gums?
Poor oral hygiene causes plaque buildup. For example, dental plaque causes bleeding gums when you skip brushing. Consequently, bacteria collect along the gum line. As a result, it leads to gum inflammation or gingivitis (inflammation of the gums).
According to PubMed, brushing too vigorously can also injure gum tissue.
Gum disease symptoms (red, swollen, or tender gums) also cause bleeding gums. Furthermore, if you do not treat gingivitis, it can progress into periodontitis.
Other medical conditions can lead to hemorrhaging gums. For instance, diabetes reduces blood flow to gums and impairs healing. Likewise, a vitamin C or vitamin K deficiency weakens blood vessels. Therefore, gums bleed more easily.
Additionally, clotting problems (e.g., platelet disorders) can trigger gum bleeding, as noted by NIH.
Certain medications such as blood thinners increase bleeding risk. Consequently, you may see bleeding gums when brushing.
Smoking and tobacco use worsen gum health. Tobacco use lowers blood flow in gum tissue. Therefore, gums do not heal well. Hence, quitting smoking can improve your overall gum health.
Hormonal changes can also cause gum bleeding. For example, during pregnancy, rising hormones can lead to swollen gums and easy bleeding.
Similarly, puberty can trigger gum changes. Likewise, menopause can reduce bone density in the jaw. As a result, women may notice more gum bleeding at these stages.
Sometimes, leukemia relate to bleeding gums.
Other causes include:
- Stress
- HIV/AIDS
- Oral herpes
- Hemophilia
- Thrombocytopenia
- Pernicious anemia
- Von Willebrand disease
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Bleeding gums often show these gum disease symptoms:
- Gums that look red or swollen.
- Bleeding when you brush or floss.
- Persistent gum infection or soreness.
- Bad breath or a bad taste in your mouth.
- Receding gums or loose teeth in advanced cases.
If you notice these signs for more than two weeks, see a dentist.
Dentists will check pocket depth around teeth. Pockets deeper than 3 mm often signal periodontitis.
They also take X-rays to check bone loss. Early diagnosis can halt gum disease progression.
Moreover, NHS advises you to visit dentist regularly for checkups. In addition, NHS reminds you to brush twice a day and clean between your teeth.
Home Care and Natural Treatments to Stop Bleeding Gums
You can find proven home treatments in our previous article, “7 Home Remedies for Bleeding Gums: Science-Based Natural Tips That Work”.
The post covers methods like saltwater mouth rinse, oil pulling, turmeric paste, aloe vera gel, and more. It also explains how to use gentle brushing and dental flossing correctly for gingivitis treatment.
If you need step-by-step guidance on home remedies for gum bleeding, visit above link.
Here, we focus on overall care, prevention, and when to seek professional help.
Professional Treatments for Gum Disease
In some cases, dentists may consult these treatments for gum disease.
Antibiotic Therapy
- Dentists may apply antibiotic gels directly into gum pockets.
- They may also prescribe oral antibiotics to reduce bacteria.
This cure is used for mild to moderate gum infections, often as a first step or alongside cleaning.
Scaling and Root Planing (Deep Cleaning)
This treatment is often used when gums are red, swollen, or bleed easily. These symptoms may be signs of gingivitis or early periodontitis (gum) disease.
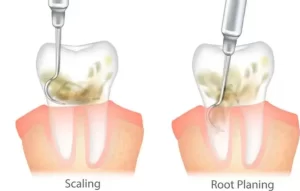 Scaling is a deep cleaning that removes hardened plaque (called tartar) from above and below the gum line.
Scaling is a deep cleaning that removes hardened plaque (called tartar) from above and below the gum line.
Root planing smooths the surface of the tooth roots. This method helps the gums stick back to the teeth and heal properly.
Both treatments reduce infection, shrink gum pockets, and prevent the disease from getting worse.
Gum Surgery
This method is used in advanced periodontitis when deep infection and tissue damage occur.
Two common types of gum surgery include:
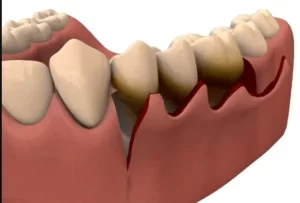 Flap Surgery (Traditional Gum Surgery)
Flap Surgery (Traditional Gum Surgery)
A dentist makes small cuts in the gums to lift back the tissue. This step allows deep cleaning of the roots and removal of hardened plaque and bacteria.
After cleaning, the gums are stitched back in place to heal tightly around the teeth.
Laser Periodontal Surgery
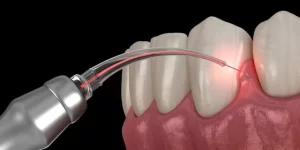 A less invasive option where a dental laser removes diseased tissue and bacteria without cutting. This method reduces pain, bleeding, and healing time.
A less invasive option where a dental laser removes diseased tissue and bacteria without cutting. This method reduces pain, bleeding, and healing time.
Both surgeries help shrink deep pockets, reattach healthy gums, and prevent tooth loss.
Bone and Tissue Grafts
This approach is used in severe gum disease when the gums or bone around the teeth are badly damaged.
Bone Grafts
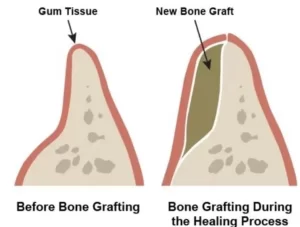 A bone graft adds new bone to parts of your jaw where bone has been lost due to gum disease.
A bone graft adds new bone to parts of your jaw where bone has been lost due to gum disease.
The dentist inserts small pieces of bone (from your body, a donor, or synthetic material) into the damaged area. Over time, your body grows new bone around it. This makes the jaw stronger and helps keep your teeth firm and in place.
Tissue Grafts
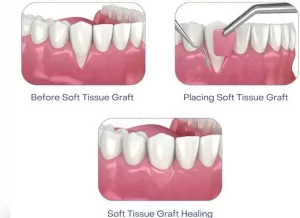 A tissue graft replaces or rebuilds gum tissue that has pulled away from the teeth (called gum recession).
A tissue graft replaces or rebuilds gum tissue that has pulled away from the teeth (called gum recession).
The dentist takes a small piece of healthy gum tissue, usually from the roof of your mouth, and places it where it’s needed. This helps cover exposed roots, protect your teeth, and make your gums look healthier.
Important Notes
Always inform your dentist about your full medical history, including any clotting problems.
If you have diabetes, your dentist will coordinate care plan with your physician. If you’re taking blood-thinning medications, they’ll work with your doctor before treatment.
How to Keep Your Gums Healthy
It’s much easier to prevent gum disease than to treat it once it gets worse. Follow these oral hygiene tips for gum disease prevention.
Brush Twice a Day
Use a soft toothbrush and brush gently in small circles.
Hold your brush at a 45-degree angle to clean along the gum line without hurting your gums.
Clean Between Your Teeth
Floss once every day to remove plaque stuck between your teeth. If you have bigger gaps, try interdental brushes or water flossers to clean better.
Use an Antiseptic Mouthwash
Rinse your mouth daily with a mouthwash that kills bacteria. This helps stop plaque buildup and keeps your gums healthy.
Replace Your Toothbrush Regularly
Change your toothbrush every three months or sooner if you’ve been sick. Old brushes don’t clean well and may carry germs.
Visit Your Dentist
Go for regular checkups and cleanings at least twice a year. Dentists can see early signs of gum problems and help prevent serious issues.
Monitor your gums closely
Watch your gums for swelling, pulling back (receding), or bleeding that happens often. If you notice these signs, improve your oral care and see a dentist.
Nutrition and Lifestyle Tips for Healthy Gums
Good diet and habits are important to gum health.
Do regular exercise
Exercise improves blood flow, bringing nutrients and oxygen to your gums. This helps keep gums and teeth healthy.
Hydration
Drinking enough water washes away food particles and bacteria. Water helps produce saliva. Saliva protects the gums from harmful acids and infections.
Add omega-3 fatty acids to your diet
Foods such as salmon, flaxseeds, and walnuts reduce gum inflammation and support healing.
A study showed omega-3s lower gum inflammation. Thus, include these foods regularly.
Eat foods rich in vitamin K
Vitamin K helps your blood clot properly, which can prevent gum bleeding. Eating kale, spinach, and broccoli daily benefits your gum health.
Include plenty of vitamin C
Vitamin C is essential for healing gum tissue. Oranges, strawberries, and bell peppers are great sources of vitamin C.
Avoid tobacco and excessive alcohol
These habits weaken your gums and increase the risk of gum disease. Quitting them will benefits gum health.
Conclusion
You should always observe the symptoms of bleeding gums. They may be an early sign of gum disease such as gingivitis or even periodontitis.
With proper oral hygiene tips, early care, and professional treatment, you can stop gum bleeding and protect your smile. Whether it’s through daily brushing, flossing, lifestyle changes, or dental visits, taking action can help you prevent gum disease. Prioritize your gum health now to avoid pain, tooth loss, and further complications.
You may also explore: Boost Metabolism and Engergy Naturally
Frequently Asked Questions
How to stop bleeding gums?
Learn simple daily habits like gentle brushing, flossing, and saltwater rinses. If bleeding persists, see a dentist. They can check for gum disease or periodontitis.
Why do my gums bleed when I brush?
Bleeding can come from brushing too hard or early gum disease (gingivitis). Other health issues may also cause bleeding gums.
Can bleeding gums heal on their own?
Mild gum inflammation from poor hygiene can heal at home. Follow oral hygiene tips and use natural remedies. But persistent bleeding may signal gingivitis or gum infection. Therefore, professional treatment is necessary.
When should I see a dentist for bleeding gums?
If your gums bleed for more than two weeks, even after improving your brushing and flossing habits, it’s time to see a dentist.
Ongoing bleeding may signal gingivitis, gum infection, or even periodontitis. Early dental care can stop the problem before it gets worse.
What are gum disease symptoms?
Red, swollen, or bleeding gums, bad breath, and loose teeth are common symptoms. Advanced disease can cause gum recession and bone loss.
Are there home remedies for gum bleeding?
Yes, natural treatments like oil pulling and turmeric can help. See our detailed guide for safe home remedies.
References:









